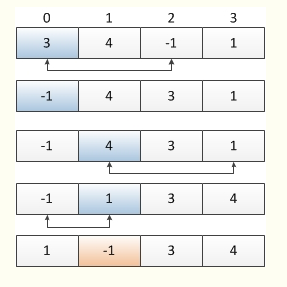
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| package com.leetcode;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class CombinationSum39 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<List<Integer>> lists = new Solution().combinationSum(new int[]{2, 7, 6, 3, 5, 1}, 9);
lists.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println(lists.size());
}
static class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
generatePath(Arrays.stream(candidates).sorted().toArray(), 0, target, new LinkedList<>(), res);
return res;
}
private void generatePath(int[] candidates, int start, int target, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> allPath) {
boolean deletedLastPath = false;
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (target - candidates[i] == 0) {
path.add(candidates[i]);
allPath.add(new LinkedList<>(path));
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
break;
} else if (target - candidates[i] > 0) {
path.add(candidates[i]);
generatePath(candidates, i, target - candidates[i], path, allPath);
}else{
if (!deletedLastPath) {
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
deletedLastPath = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
|